Now, let's talk about validation. What happens if the user doesn't pass anything?
First, let's see what we get if we don't send the name field.
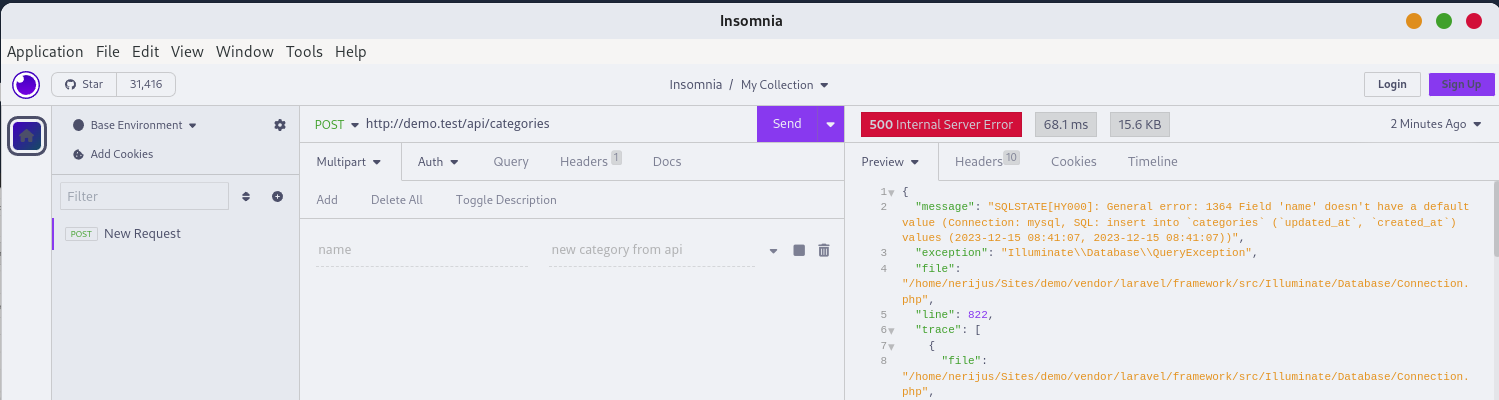
We get a 500 error code and a SQL error message, which is also a security issue. We don't want customers to see the actual error.
For the backend part, we can validate the regular way using Form Request.
php artisan make:request StoreCategoryRequestapp/Http/Requests/StoreCategoryRequest.php:
class StoreCategoryRequest extends FormRequest{ public function authorize(): bool { return true; } public function rules(): array { return [ 'name' => ['required'] ]; }}app/Http/Controllers/Api/CategoryController.php:
use App\Http\Requests\StoreCategoryRequest; class CategoryController extends Controller{ // ... public function store(Request $request) public function store(StoreCategoryRequest $request) { $category = Category::create($request->all()); return new CategoryResource($category); }}Now, we see a better result that can be shown for the user in the browser. The status code is 422, a default validation code.

We can use the catch in the Vue component to catch the errors.
<template> // ...</template> <script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'; const name = ref('') const submit = () => { axios.post('/api/categories', { name: name.value }) .then(response => { console.log('New Category ID: ' + response.data.data.id) }) .catch(error => { console.log(error.response.data.errors) }) }</script>We see two errors if we try to post from the Vue.js app in the console. The first is what the browser shows and the second is from the console log.

As a Laravel developer working on a backend job, you must send a 422 status with validation messages.
The tutorial does not say how to fill out the
StoreCategoryRequest.php, I don't know if it is relevant to place the content that produces the image result.Wow. Don't know how I missed this. Thanks. Added.
Hi, how to can i customize error message format in laravel 11 ?
If you are using form requests then the same way. Nothing changed with laravel 11
Laravel Validation returns an error as a JSON response with the error messages in a strict standard format. What if you want to change it to an entirely different structure because your front-enders ask you for specific key-value pairs? I found this article wicth is based on laravel 10 //post/laravel-validation-completely-customize-error-message-format. But with laravel 11, there is bootstrap folder which manages exceptions, middleware and others ...
You do the same in the bootstrap/app.