The next thing we'll work on is adding real estate properties: houses/homes to rent. In this particular lesson, we will focus on adding the geographical data for city, country, and latitude/longitude.
Goals of This Lesson
- Build a DB schema for countries, cities, and geographical objects, seeding a few of each
- Build a first version of DB schema for properties, with geographical data
- Automatically set property latitude/longitude based on the address, with Observer and Google Maps API
- First version of API endpoint to create a property, covered by PHPUnit test
By the end of this lesson, we will see this in Postman:
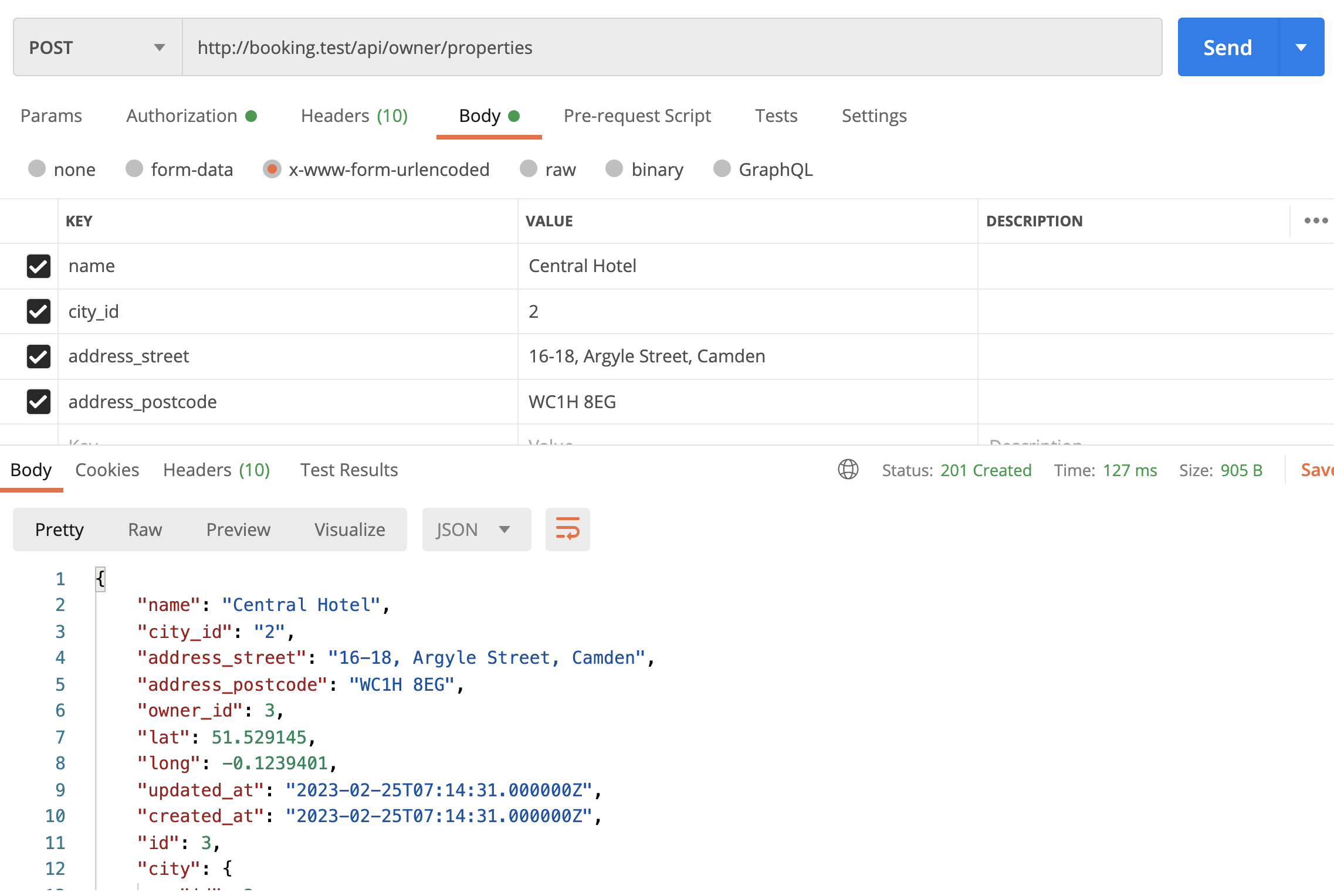
Geo Coordinates: Countries / Cities / Famous Objects
First, let's add the latitude and longitude columns to the DB table of countries.
php artisan make:migration add_geocoordinates_to_countries_tableMigration file:
Schema::table('countries', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->after('name', function() use ($table) { $table->decimal('lat', 10, 7)->nullable(); $table->decimal('long', 10, 7)->nullable(); });});Next, we will definitely build a search by city, so we need a model for that as well, with coordinates.
php artisan make:model City -msapp/Models/City.php:
class City extends Model{ use HasFactory; protected $fillable = ['country_id', 'name', 'lat', 'long']; public function country() { return $this->belongsTo(Country::class); }}Migration file:
Schema::create('cities', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('country_id')->constrained(); $table->string('name'); $table->decimal('lat', 10, 7)->nullable(); $table->decimal('long', 10, 7)->nullable(); $table->timestamps();});Finally, let's create a separate database table for geographical objects, such as "Big Ben" or "Statue of Liberty", cause people often search by them.

php artisan make:model Geoobject -msapp/Models/Geoobject.php:
class Geoobject extends Model{ use HasFactory; protected $fillable = ['city_id', 'name', 'lat', 'long'];}Migration file:
Schema::create('geoobjects', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('city_id')->nullable()->constrained(); $table->string('name'); $table->decimal('lat', 10, 7)->nullable(); $table->decimal('long', 10, 7)->nullable(); $table->timestamps();});Next, let's build the Seeders for all those new tables. We will use them to automatically run seeds in our automated tests, too. So, we fill in a few countries, a few cities, and a few geographical objects.
php artisan make:seeder CitySeederphp artisan make:seeder GeoobjectSeederCountry seeder already existed, we just need to fill it with data.
database/seeders/CountrySeeder.php:
use App\Models\Country; class CountrySeeder extends Seeder{ public function run() { Country::create([ 'name' => 'United States', 'lat' => 37.09024, 'long' => -95.712891 ]); Country::create([ 'name' => 'United Kingdom', 'lat' => 55.378051, 'long' => -3.435973 ]); }}database/seeders/CitySeeder.php:
use App\Models\City; class CitySeeder extends Seeder{ public function run() { City::create([ 'country_id' => 1, 'name' => 'New York', 'lat' => 40.712776, 'long' => -74.005974, ]); City::create([ 'country_id' => 2, 'name' => 'London', 'lat' => 51.507351, 'long' => -0.127758, ]); }}database/seeders/GeoobjectSeeder.php:
use App\Models\Geoobject; class GeoobjectSeeder extends Seeder{ public function run() { Geoobject::create([ 'city_id' => 1, 'name' => 'Statue of Liberty', 'lat' => 40.689247, 'long' => -74.044502 ]); Geoobject::create([ 'city_id' => 2, 'name' => 'Big Ben', 'lat' => 51.500729, 'long' => -0.124625 ]); }}Then we, of course, add them all to the main DatabaseSeeder, which now will look like this:
class DatabaseSeeder extends Seeder{ public function run() { $this->call(RoleSeeder::class); $this->call(AdminUserSeeder::class); $this->call(PermissionSeeder::class); $this->call(CountrySeeder::class); $this->call(CitySeeder::class); $this->call(GeoobjectSeeder::class); }}Great, now we have some geographical entities to play around with, now let's go to the actual properties!
Properties DB Table with Auto-Coordinates
We create a model/migration/seeder for our "main" table of the project:
php artisan make:model Property -msAnd here's the schema with the main fields, for now. There will be more, but at the moment, we focus on geographical things for the search, remember?
Schema::create('properties', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('owner_id')->constrained('users'); $table->string('name'); $table->foreignId('city_id')->constrained(); $table->string('address_street'); $table->string('address_postcode')->nullable(); $table->decimal('lat', 10, 7)->nullable(); $table->decimal('long', 10, 7)->nullable(); $table->timestamps();});And the model should contain those fields as fillable.
app/Models/Property.php:
class Property extends Model{ use HasFactory; protected $fillable = [ 'owner_id', 'name', 'city_id', 'address_street', 'address_postcode', 'lat', 'long', ]; public function city() { return $this->belongsTo(City::class); }}Now, when someone enters a new property, wouldn't it be nice if lat/long fields would be automatically populated, by street address?
I have a separate tutorial on how to do that with Google Maps API (warning: API is not free!), and will make a re-cap of it here in this lesson.
We will use a package called GeocoderLaravel that allows you to easily integrate Google Maps API in your Laravel project.
composer require toin0u/geocoder-laravelphp artisan vendor:publish --provider="Geocoder\Laravel\Providers\GeocoderService"Then, we add the Google Maps API key (read here how to get it) to the .env file:
GOOGLE_MAPS_API_KEY=AIzaSyAWRsRGOFbTXRlLHDOSudkerLjUtBfElUtAnd then, we just need to call these lines to convert the address into coordinates:
$result = app('geocoder')->geocode($address)->get();$coordinates = $result[0]->getCoordinates();$lat = $coordinates->getLatitude();$long = $coordinates->getLongitude();To automate all this process, we create an Observer file, to watch for the creation of the new Properties.
php artisan make:observer PropertyObserver --model=Propertyapp/Observers/PropertyObserver.php:
use App\Models\Property; class PropertyObserver{ public function creating(Property $property) { // We also add the owner automatically if (auth()->check()) { $property->owner_id = auth()->id(); } if (is_null($property->lat) && is_null($property->long)) { $fullAddress = $property->address_street . ', ' . $property->address_postcode . ', ' . $property->city->name . ', ' . $property->city->country->name; $result = app('geocoder')->geocode($fullAddress)->get(); if ($result->isNotEmpty()) { $coordinates = $result[0]->getCoordinates(); $property->lat = $coordinates->getLatitude(); $property->long = $coordinates->getLongitude(); } } }}Finally, we register that Observer, let's do it directly in the Model.
app/Models/Property.php:
use App\Observers\PropertyObserver; class Property extends Model{ // ... public static function booted() { parent::booted(); self::observe(PropertyObserver::class); }}Great, now whenever someone creates a new Property, coordinates should be auto-filled.
Creating Property: Route/Controller/Request
Now, let's build a Controller/Route to create a new property, and add a Form Request immediately, too.
php artisan make:controller Owner/PropertyControllerphp artisan make:request StorePropertyRequestapp/Http/Controllers/Owner/PropertyController.php:
namespace App\Http\Controllers\Owner; use App\Http\Requests\StorePropertyRequest;use App\Models\Property; class PropertyController extends Controller{ // ... public function store(StorePropertyRequest $request) { $this->authorize('properties-manage'); return Property::create($request->validated()); }}app/Http/Requests/StorePropertyRequest.php:
class StorePropertyRequest extends FormRequest{ public function authorize() { return true; } public function rules() { return [ 'name' => 'required', 'city_id' => 'required|exists:cities,id', 'address_street' => 'required', 'address_postcode' => 'required', ]; }}As you can see, we require only the name/city/address, as owner/lat/long will be filled automatically by the Observer.
Finally, the new route:
Route::middleware('auth:sanctum')->group(function () { // ... Route::post('owner/properties', [\App\Http\Controllers\Owner\PropertyController::class, 'store']); });We try it out in Postman:

Finally, in this lesson, let's add the automatic test that it actually works.
tests/Feature/PropertiesTest.php:
namespace Tests\Feature; class PropertiesTest extends TestCase{ // ... public function test_property_owner_can_add_property() { $owner = User::factory()->create(['role_id' => Role::ROLE_OWNER]); $response = $this->actingAs($owner)->postJson('/api/owner/properties', [ 'name' => 'My property', 'city_id' => City::value('id'), 'address_street' => 'Street Address 1', 'address_postcode' => '12345', ]); $response->assertSuccessful(); $response->assertJsonFragment(['name' => 'My property']); }}A debatable question is whether we should leave the auto-coordinates enabled while testing. Probably not, as we don't want to get charged for Google API every time we run automated tests, right?
So, this is how I disable that part of the Observer:
app/Observers/PropertyObserver.php:
class PropertyObserver{ public function creating(Property $property) { if (is_null($property->lat) && is_null($property->long) && !(app()->environment('testing'))) { // ... getting the coordinates } }}In other words, while testing, if we don't provide the lat/long for the new property, the coordinates will remain NULL, which is fine.

We may create another Unit test that will assert that the API works or Mock/Fake data, but this is outside of the scope of this course. For that, please read the tutorial Laravel Testing: Mocking/Faking External 3rd Party APIs .
Like this very much; however we in the United States use states more than country. I see you used the United States and New York City bot you left out the states of New York. Country_id, State_id, and city_id then the address and zip code is used to mail a letter hear the country is only used if mailing from out side of the United States.
I agree, but I think the main point of this scenario was to copy what he saw on bookings.com In either case you would be able to adapt what he has created to your specific case.
I know, and in other countries there's a different regional structure, too. But if I went that deep with every country, and other Booking.com features with all their possible details, I wouldn't release this course until 2026.
Not sure what to say about the OP lol
In (test_property_owner_can_add_property) (PropertiesTest)
You should add assignRole in: $owner = User::factory()->create(['role_id' => Role::ROLE_OWNER])
It will be like this: $owner = User::factory()->create(['role_id' => Role::ROLE_OWNER])->assignRole(Role::ROLE_OWNER);
I think you forget to add
Thanks for the comment. If you mean I should assign it with Spatie package, then getting back to the earlier lesson, I used Spatie only as a separate demo example in a separate branch, but I won't use that example for the other course lessons.
it is actually $owner = User::factory()->create()->assignRole(Role::ROLE_OWNER); not $owner = User::factory()->create(['role_id' => Role::ROLE_OWNER])->assignRole(Role::ROLE_OWNER); it will still throw an error
At this section I got an error when I tried to do composer require toin0u/geocoder-laravel.
ERROR -> Your requirements could not be resolved to an installable set of packages.
I've been using PHP 8.1.16 and the project it was created with Laravel 10.8...
Not sure, the
composer.jsonof that package shows PHP 8.0+ and Laravel 10 supported.Are you sure you're on PHP 8.1? Have you tried to run
phpinfo()function in your webpage? Because sometimes there are different PHP versions for CLI and websites.I got thesame error while installing the toin0u/geocoder-laravel in my project PHP 8.1.13
Pls Have your solved our own error and how did you solve
Ok I can confirm that the underlying package doesn't support PHP 8 yet. It's very weird, so how could it work for me when preparing for this course just a few months ago...
Anyway, you can wait for them to update, or use some alternative like Spatie Geocoder, or skip that geocoding part of the course, for now.
Use the option --with-all-dependencies (-W) to allow upgrades, downgrades and removals for packages currently locked to specific versions.
@haritjahjo I was getting the same error, it loaded when I added the -W parameter, thank you.
Hi, everyone pls i have been getting 500 error message; showing this General error: 1364 Field 'owner_id' doesn't have a default value (Connection: mysql, SQL: insert into
properties(name,city_id,address_street,address_postcode,lat,long,updated_at,created_at) values (Central Hotel, 4, 16-18, Argyle Street Camden, WC1H 8EG, 51.529145, -0.1239401, 2023-05-21 23:08:59, 2023-05-21 23:08:59)) And why this is in property table $table->foreignId('owner_id')->constrained('users');Hi, I replied to you via email. The field
owner_idis auto-set in thecreating()method of the Observer.yes i thank you i have seen it
Hello, I have 1 question. What if I allow the owner to select property location on google map api market. and get the lat, long from the api. Is google will give me the city, country names and address ?! Because I fill in some casese the user will not know what is the full address name, so mayble google will give us wrong lat & long. What u think?
Thanks
Yes it is possible with Google Maps API but it's not free. We have an article about it: Laravel: Find Addresses with Coordinates via Google Maps API
Thanks yeah i know its paid API, but it's powerful api. The tutorial awesome.
Sorry but I have a long question here,
If I wanna scale the website to Chalets, Cars, Appartement with Yachts, as you know i will have too much duplicated columns if i wanna create table for each one.
So your Property Model will fix this issue, but here you created Appartement model with hasOne relationship. what if I want to create Chalet and Yacht Models and the Parent Model is Property. It will be very useful because all the models is rental base.
How to make the relationship here.
It's a personal preference how to structure, as only you know how many columns will be the same or different how often you would query them, etc.
Wouldn't it be better to still use Apartment for chalets/cars/yachts, just with different Apartment Type?
Yes it's possible, i will see thanks.
The Postman screenshot shows the property record inserted, but also the city details. This should be added in order to see it: return Property::create($request->validated())->load("city");
I change the PropertyObserver for Spatie Geocoder:
It would probably be better to ignore the 'eloquent.creating: App\Models\Property' event in the test than to add redundant conditions to the PropertyObserver. We will be frank: altering the code being tested for the needs of the test is a bad practice.